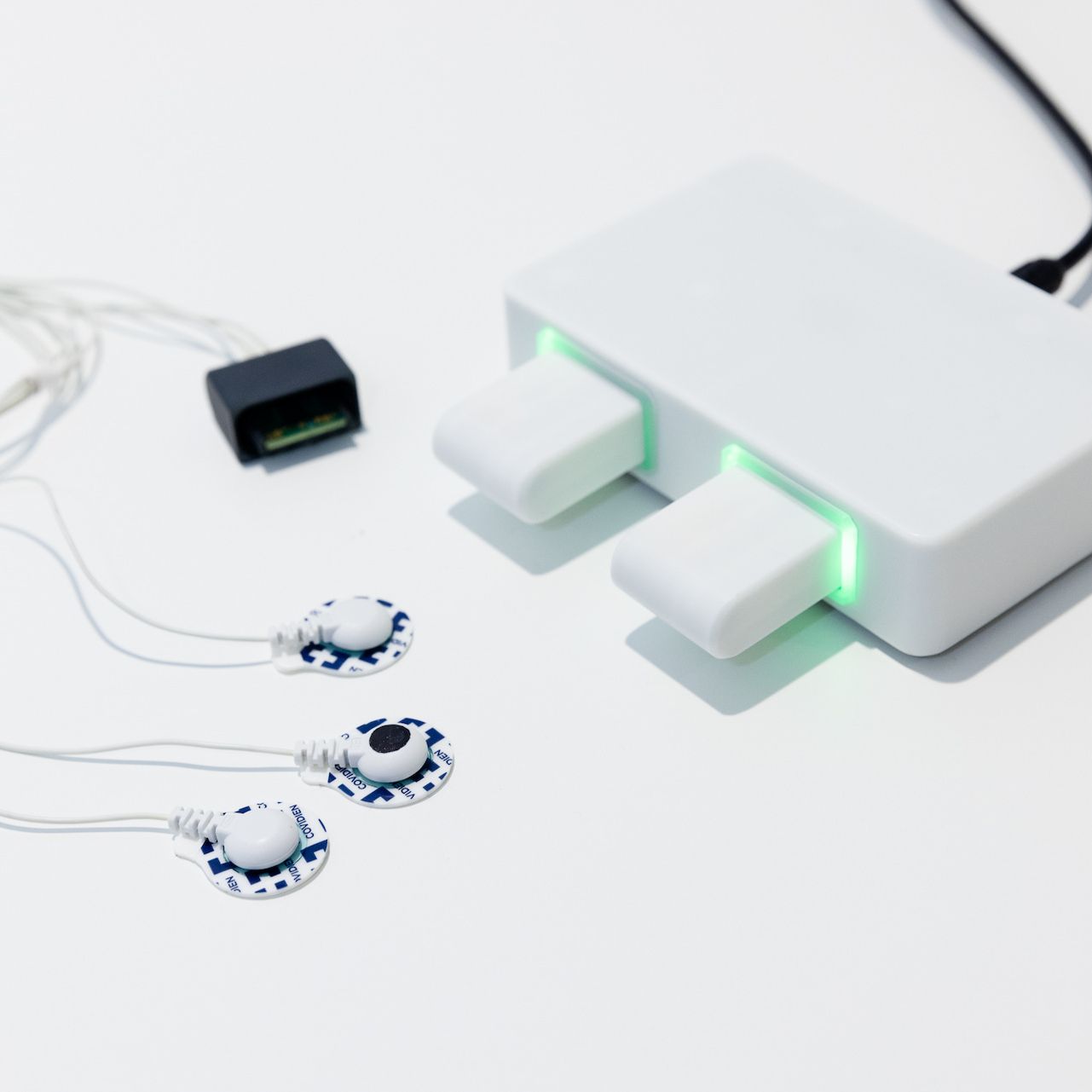

Non-Invasive Insight
Surface EMG of the diaphragm offers direct, non-invasive access to neural respiratory drive. This is ideal for dynamic patient monitoring.
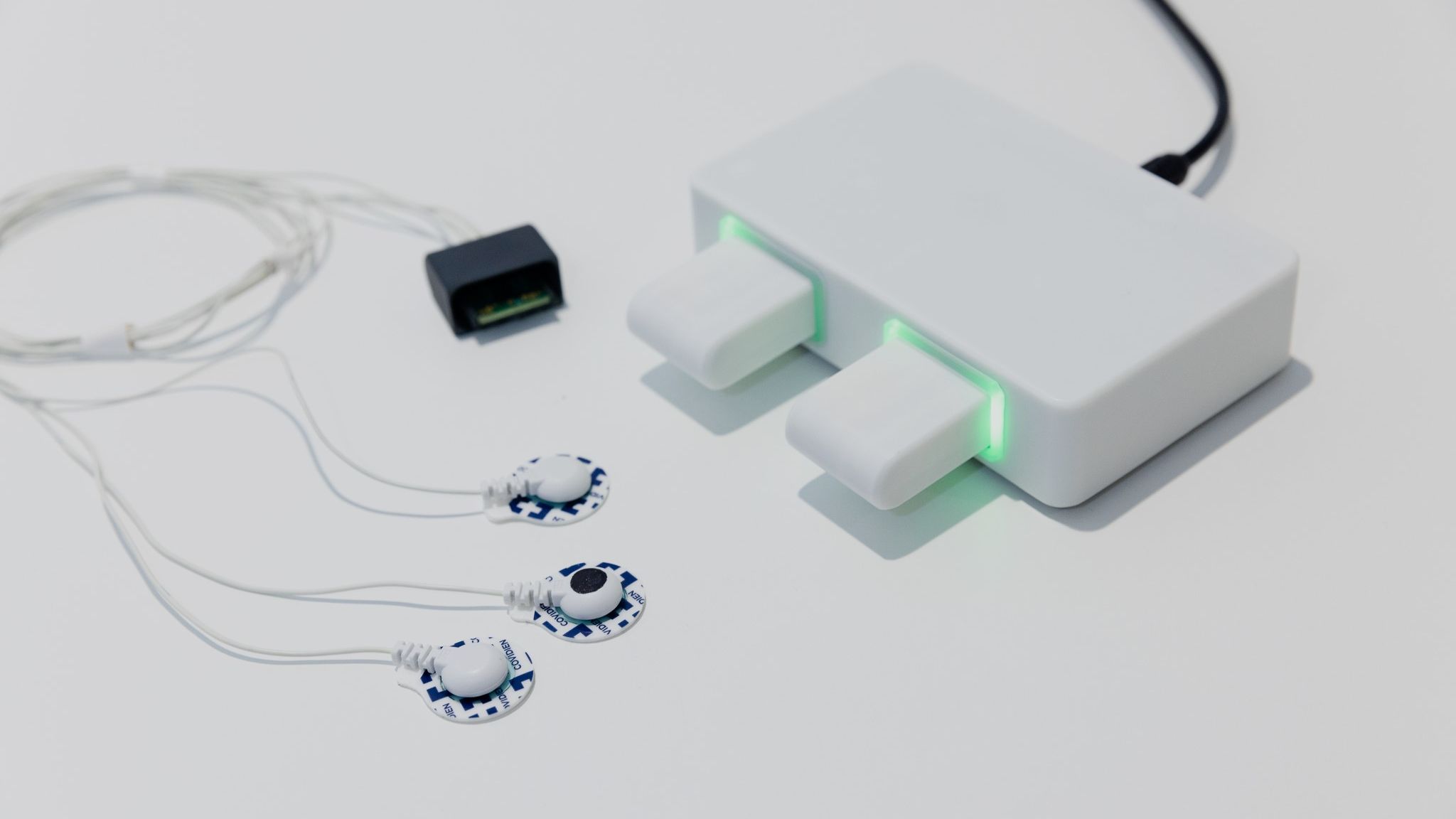

Macawi SERA is widely applicable across care settings supports personalized therapy, patient-specific tuning, and responsive treatment.
Patient-ventilator asynchrony (PVA) occurs when the ventilator’s timing or pattern doesn’t align with the patient’s own breathing effort. This mismatch is common across all ventilation modes and is linked to longer ICU stays and lower weaning success rates.
Diaphragm sEMG enables near-instant detection of inspiration onset, offering a reliable triggering signal that reflects the patient’s true respiratory intent. This improves synchronization, reduces the need for complex ventilator settings, and minimizes reliance on specialist training—making therapy more responsive and intuitive.

Standard weaning strategies like SBT have limited success rates. Real-time diaphragm activity metrics (e.g., EMG amplitude, AUC) offer objective insight into work of breathing and fatigue—supporting more accurate weaning decisions and reducing complications.
Conventional ventilation delivers fixed support, risking under- or over-assistance.
sEMG-guided proportional support dynamically adjusts to the patient’s effort, reducing fatigue and improving respiratory efficiency—validated in systems like NAVA and PAV+.

Surface EMG of the diaphragm offers direct, non-invasive access to neural respiratory drive. This is ideal for dynamic patient monitoring.
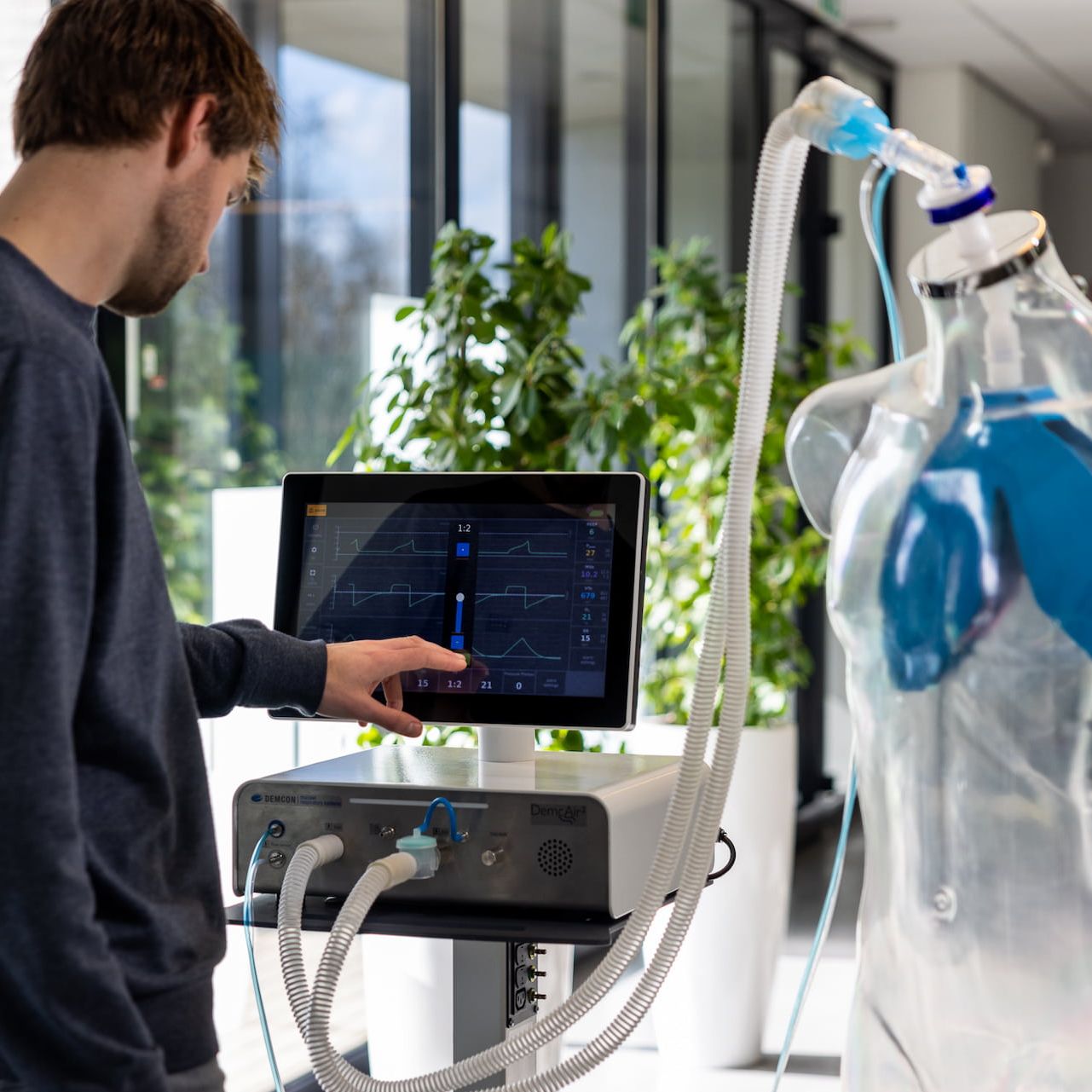

Real-time monitoring of neural respiratory drive enhances understanding of patient condition and therapy response.
Dual-function sEMG monitoring of diaphragm and heart—SERA enables precise, non-invasive cardiorespiratory insights.
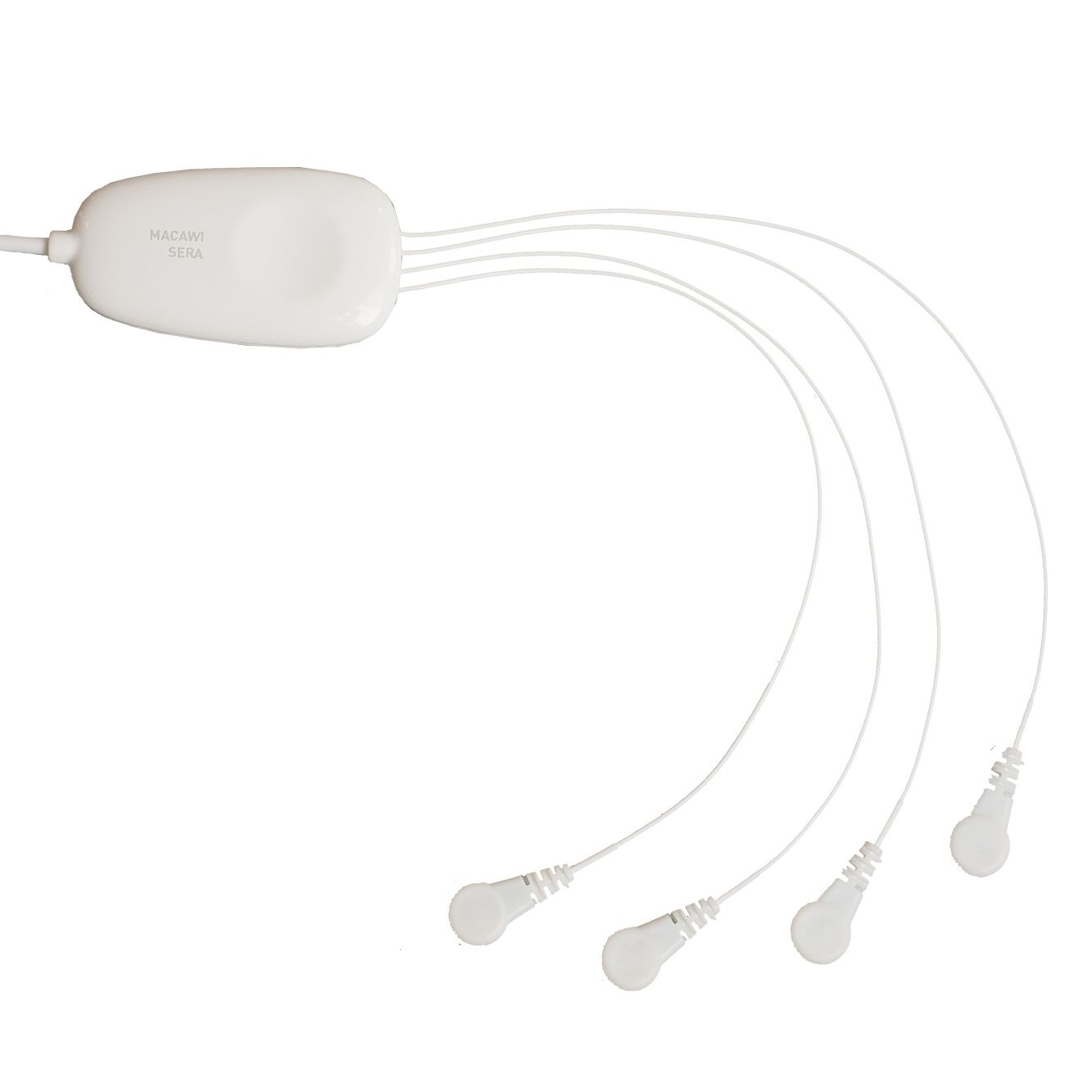

Intuitive setup with familiar ECG-like design, just one extra lead for powerful dual-function monitoring.
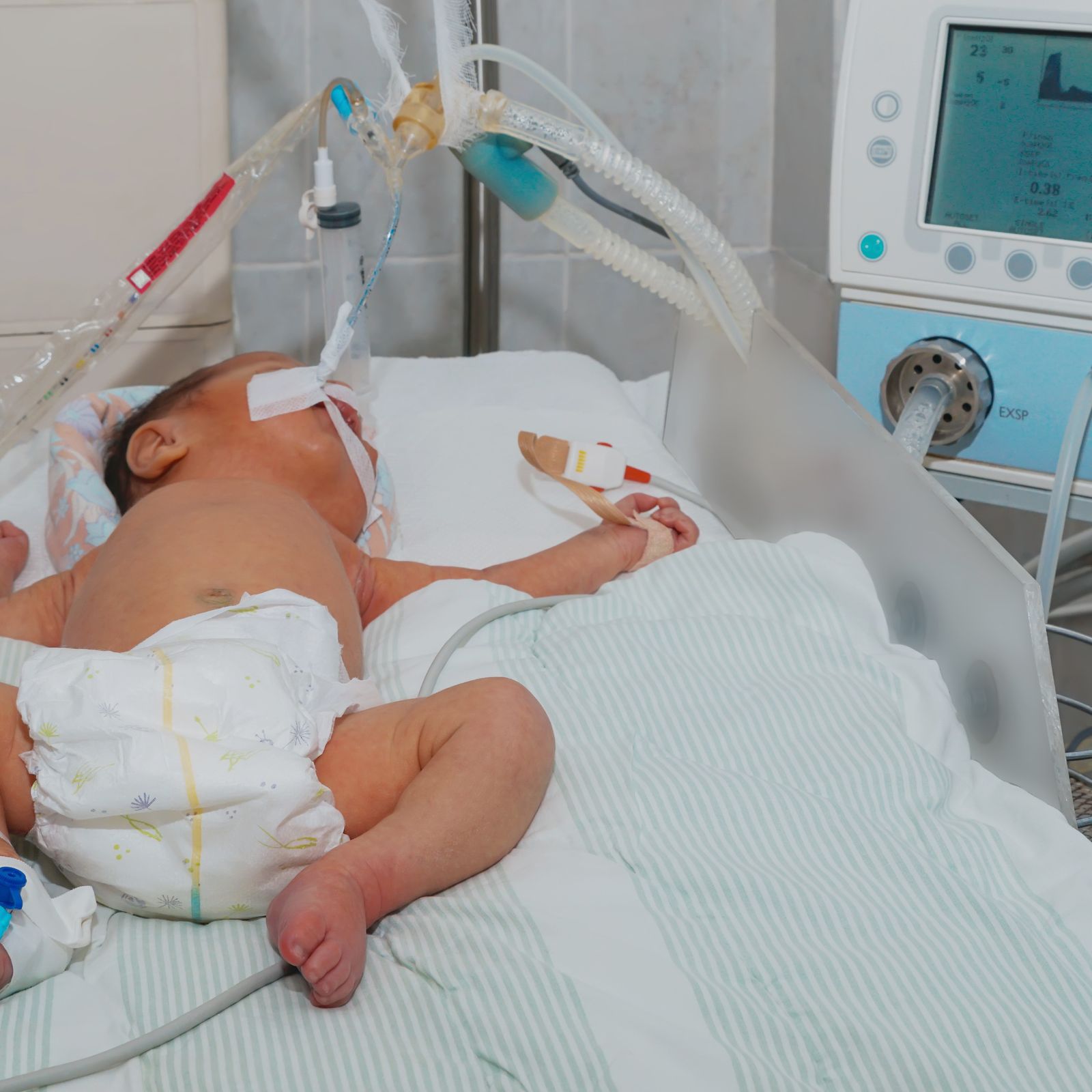
The Macawi SERA sensor can be used in all patient groups. Ranging from the smallest preterms to the largest adults in ICU-environments.